- general description
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Prevention
- Treatment in mainstream medicine
- Healthy foods
- ethnoscience
- Dangerous and harmful products
- Information sources
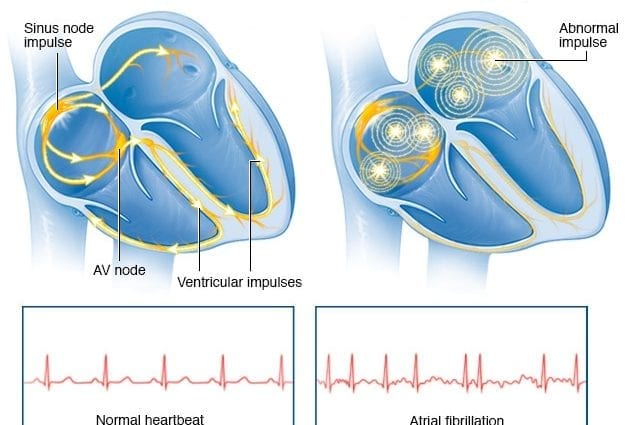
General description of the disease
It is one of the most common heart conditions affecting millions of people around the world. People over 60 are at risk. The development of atrial fibrillation (AF) provokes heart failure.
With atrial fibrillation, the patient’s heart rhythm is disturbed, while frequent atrial contractions occur, their frequency can be up to 500 beats per minute.
Depending on the frequency of atrial contraction, AF is classified into:
- bradysystolic – no more than 60 cuts per minute;
- normosystolic – 60-90 atrial contractions;
- tachystolic – over 90 atrial contractions in 60 seconds.
Depending on the symptomatology and characteristics of the course of the pathology, fibrillation is classified into:
- chronic form – a long course of the disease with pronounced symptoms;
- persistent form – if the illness lasts more than 7 days;
- paroxysmal form – attacks lasting no more than 5 days.
Fibrillation causes
The main reason for the presented pathology is a failure of the order of ventricular contractions [3]… With atrial fibrillation, the atrial contraction is not at the same frequency as in a healthy person, but in inconsistency, therefore, instead of a powerful push, a small tremor is obtained and the required amount of blood does not enter the ventricles.
Factors provoking the development of arrhythmia may be cordial and unhearted… Cardiac causes include:
- 1 hypertension – with high blood pressure, the heart muscle functions in an enhanced mode, subsequently ceases to cope with the load and stretches;
- 2 tumors in the heart – interfere with the signal transmission;
- 3 heart surgery – in place of the cells of the conducting system, postoperative scars are formed, and nerve impulses pass in other ways;
- 4 pathology of the heart – heart defects, heart attack, heart failure.
Noncardiac factors that can cause AF:
- 1 electric shock;
- 2 sleep apnea;
- 3 viral diseases;
- 4 overweight;
- 5 alcohol abuse;
- 6 uncontrolled intake of certain medications;
- 7 pathology of the lungs, kidneys and thyroid gland;
- 8 increased stress and overwork.
Fibrillation symptoms
The characteristic signs of the disease depend, first of all, on the form of fibrillation, the state of the myocardium and the degree of damage to the heart valve.[4]… As a rule, patients with arrhythmia are worried about:
- shortness of breath even with minor physical exertion;
- baseless feeling of fear;
- tachycardia;
- feeling of a sinking heart;
- shiver;
- increased sweating;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the heart;
- dizziness up to fainting.
During an AF attack, the patient feels chest pain, tachycardia, tremors in the body, panic fear of death, and polyuremia. When sinus heart rate is restored, these symptoms disappear.[5].
Complications of fibrillation
One of the most dangerous complications of arrhythmia is ischemic stroke and other thromboembolisms – these pathologies occur in 5% of patients with AF.There are a number of factors that provoke the development of complications during fibrillation, these include:
- 1 diabetes;
- 2 age group over 70;
- 3 hypertension;
- 4 circulatory disturbance;
- 5 smoking;
- 6 congenital heart defects;
- 7 alcohol abuse.
Prophylaxis of fibrillation
The risk of developing AF can be reduced with timely therapy for heart disease. In addition, cardiologists advise adhering to the following recommendations:
- normalize body weight, since excess weight provokes the development of heart pathologies;
- quit smoking completely;
- control the level of cholesterol and blood pressure, as their elevated levels cause damage to the blood vessels;
- remember about daily physical activity: give up the elevator, walk to work, take walks on weekends;
- in case of heart disease, it is necessary to take all medications prescribed by a cardiologist;
- take psychotropic drugs with caution;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- avoid stressful situations as much as possible;
- monitor blood glucose levels.
Treatment of fibrillation in mainstream medicine
AF therapy occurs in a hospital setting, and it is important to stop the attack on time. For this, the patient is placed on a couch and the neck area is freed from clothing. Before the arrival of the doctor, the patient can be given drugs such as Corvalol or Corvaldin. With significant tachycardia, a towel soaked in cool water is applied to the patient’s forehead. In case of loss of consciousness, the victim is given a sniff of ammonia or lightly slapped on the cheeks.
After providing medical care and after stopping the attack, the patient is hospitalized, and the cardiologist diagnoses the patient, which includes:
- 1 patient complaints about heart problems;
- 2 clarification and analysis of the transferred pathologies, operations and hereditary diseases;
- 3 analyzes of blood and urine indicators;
- 4 examination of the skin and listening to the chest for heart murmurs;
- 5 analysis of indicators of thyroid hormones;
- 6 ECG and echocardiography;
- 7 chest x-ray to determine the size of the heart.
In the case when drug therapy is not enough, then they resort to surgical intervention.
Benefits for Fibrillation
Patients with atrial fibrillation are shown a diet based on plant foods or with a minimum of animal fats:
- for productive work, the heart needs magnesium, which is found in bran bread, oranges, cashews, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, sprouted wheat seeds, legumes and cereals;
- it is necessary to eat as many foods rich in vitamin K as possible: spinach, tomatoes, carrots, bananas, potatoes;
- Ca restores the work of the heart, it is found in dairy products, fish, seeds, nuts and seaweed;
- eating as many blueberries as possible as a source of antioxidants;
- dried fruits and fresh seasonal fruits are recommended as desserts, citrus fruits in winter;
- low-fat varieties of fish and meat need to be stewed or boiled;
- soups are recommended with vegetable broth;
- as additives, you can use sea buckthorn or flax seed oil;
- durum wheat pasta.
Food should be eaten in small portions in order not to overload the stomach. Eating should be finished with a feeling of slight hunger. You cannot watch TV, talk or read while eating.
Traditional medicine for fibrillation
Traditional medicine cannot cure AF, but they can be an adjunct to conventional therapy:
- 1 a mixture of honey and chopped lemon peel to use daily before meals;
- 2 prepare a decoction of hawthorn, motherwort and valerian, take within a month;
- 3 try to eat as many fresh viburnum berries as possible, and not in season steam dry berries with boiling water[1];
- 4 for 10 days in a dark place in an opaque glass container, insist on the motherwort herb alcohol, drink 10-15 drops before meals;
- 5 to improve blood circulation, drink a decoction based on calendula flowers;
- 6 during the day, drink a decoction based on rosehip berries as tea;
- 7 dill seeds and dry leaves of sunflower flowers take in equal proportions, pour boiling water, insist, filter and take ½ tbsp. several times a day;
- 8 drink at least a liter per day of a decoction of the roots of mountain celery;
- 9 chop a small head of onion and add 1 chopped green apple, take this vitamin mixture for a month;
- 10 apply a clay cake to the heart area, hold for 15 – 20 minutes;
- 11 in the fight against arrhythmia, applications of copper plates, which are applied to the skin in the heart area, are effective[2];
- 12 drink before meals 50 g of broth from the roots of mountain ash;
- 13 drink tea based on peppermint leaves;
- 14 there are more figs;
- 15 before bedtime, take 1 tsp. honey.
Dangerous and harmful products in fibrillation
With fibrillation, foods with a high cholesterol content should be excluded from the diet:
- fried foods;
- smoked meat and fish;
- rich broths;
- fatty dairy products;
- canned fish and meat;
- chicken egg yolks;
- rich pastries;
- strong tea and coffee;
- fat, meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- completely give up alcohol.
- Herbalist: golden recipes for traditional medicine / Comp. A. Markov. – M .: Eksmo; Forum, 2007 .– 928 p.
- Popov A.P. Herbal textbook. Treatment with medicinal herbs. – LLC “U-Factoria”. Yekaterinburg: 1999.— 560 p., Ill.
- Atrial fibrillation overview,
- Atrial Fibrillation, source
- Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosed through Sensory Complaints,
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!