Contents
Gouty tophus: definition, radiography, treatments
Gouty tophus is a symptom of gout disease. It is a painful inflammatory flare-up in a joint caused by a build-up of uric acid salts.
What is gouty tophus?
Gout is a disease manifested by painful inflammatory flare-ups localized in a joint. They are called gout attacks or gout attacks. Gout is the result of too much uric acid in the blood, or hyperuricemia. However, only 1 in 10 people with hyperuricaemia are likely to trigger a gout attack. This is a necessary condition, but not sufficient for the onset of the disease. It is likely that there is a genetic component to gout.
Symptoms can announce the attack of gout:
- tingling;
- discomfort;
- pain ;
- limitation of mobility;
- stiffness of the joint.
The benefit for the patient of being able to anticipate the crisis is also to be able to anticipate its anti-inflammatory treatment. The symptoms of the seizure itself are indeed much more important:
- sudden onset, often at night or at rest;
- severe pain, burning sensation in a joint;
- inflammatory joint damage (often in the legs and more particularly the big toe);
- joint red, swollen, hot, bulky, painful to touch;
- possible swelling and redness of the skin around the affected joint;
- possible gouty tophus;
- possible fever and chills.
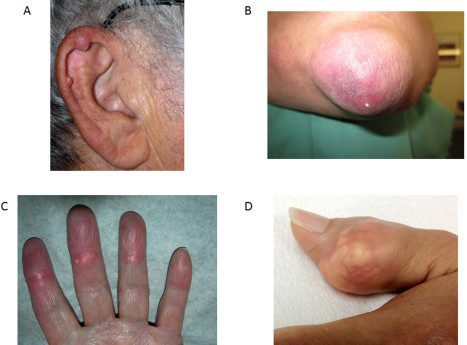
Gouty tophus is therefore a symptom of the gout attack. This is a rare clinical manifestation. It is a deposit of uric acid in the form of urate (uric acid salts) under the skin, visible around the affected joints and / or the pinna of the ear, elbows, Achilles tendons or the fingertips. It appears in the form of nodules under the skin, of a firm and voluminous consistency. The tophus is rarely at risk of infection because uric acid is unfavorable to the development of microbes.
For the diagnosis of gout, the doctor looks for the presence of tophus. This can be spotted on clinical examination. The doctor may also take an x-ray of the affected bones and joints which may show bone lesions or possible tophi around the joint. Tophus may also go unnoticed on physical examination and x-ray and be detected by joint ultrasound which shows uric acid deposits on the joint cartilage.
What are the causes ?
Tophus is a consequence of gout. This disease is caused by having too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is naturally present in the blood but at a level below 70 mg / liter. It is the consequence of certain cleansing mechanisms of the organism. It is then eliminated by the kidney, which acts as a filter.
There are two possible causes of hyperuricemia:
- hyperproduction of uric acid (consequence of a diet too rich in proteins or of a significant destruction of cells);
- decreased elimination by the kidneys (most common cause).
The following factors can cause a gout attack:
- Alcohol consumption ;
- over-consumption of foods rich in protein and fat;
- a ketoacidosis attack during diabetes;
- loss of water from the body due to intense physical exertion, dehydration, fasting, etc. ;
- a stressful situation (accident, trauma, surgery, infection, etc.);
- taking certain medications (diuretics, low-dose aspirin, starting a hypo-uricemic treatment).
What are the consequences of gout and tophus?
Leaving the disease untreated means exposing yourself to a greater risk of gout attacks, which cause very severe pain in the affected joint.
In rare cases, untreated tophus may ulcerate and release a whitish substance. We talk about tophaceae gout which occurs in a third of untreated patients within 5 years of the onset of the disease.
In the long term, gout can cause cardiovascular and kidney complications.
What treatments?
The treatment of gout has two objectives:
- treat gout attack when it occurs;
- treat the patient over the long term to reduce the occurrence of seizures.
The treatment of the seizure is aimed at relieving the pain. It begins with resting and cooling the affected joint. The doctor can then prescribe different drugs to help manage the crisis: colchicine, anti-inflammatory drugs and sometimes corticosteroids.
The aim of the basic treatment is to maintain the uric acidemia in order to prevent seizures, the formation of tophi, joint complications and the appearance of kidney stones. The first stage of treatment consists of the establishment of hygienic and dietary measures. The doctor can then set up a hypo-uricemic treatment.
Different drugs exist:
- allopurinol ;
- febuxostat;
- probenecid;
- benzbromarone.
To check the effectiveness of the basic treatment, the doctor monitors the patient’s uric acid level in order to validate that it falls below the value making it possible to obtain the dissolution of uric acid salts.
When to consult?
Gout is a chronic disease that requires lifelong treatment and multidisciplinary management, involving the attending physician, a rheumatologist, a cardiologist, a nephrologist, etc.